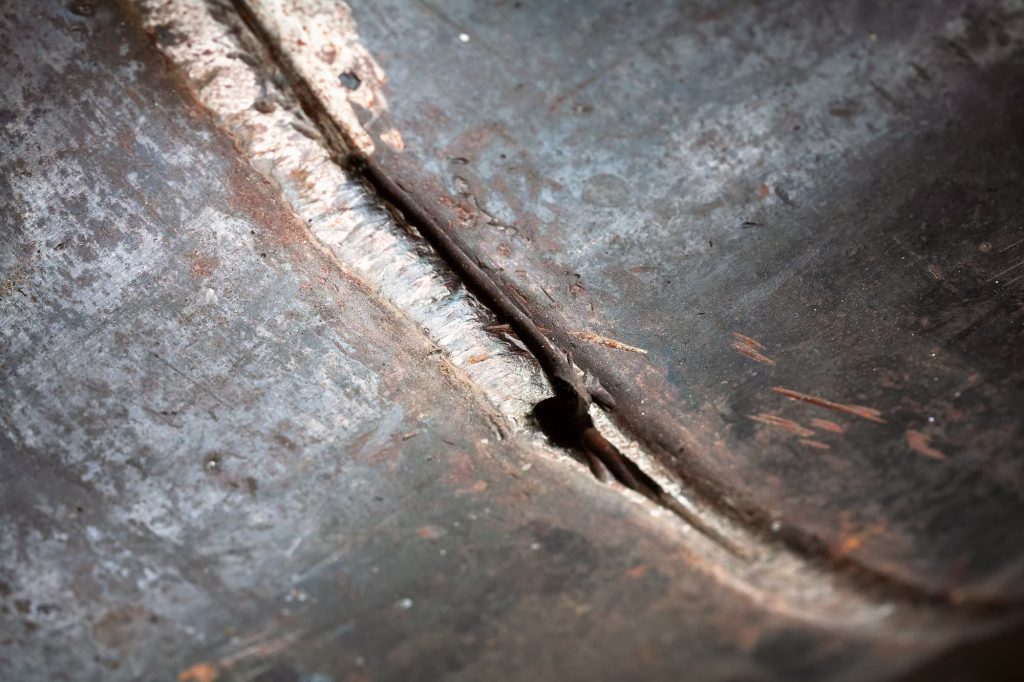
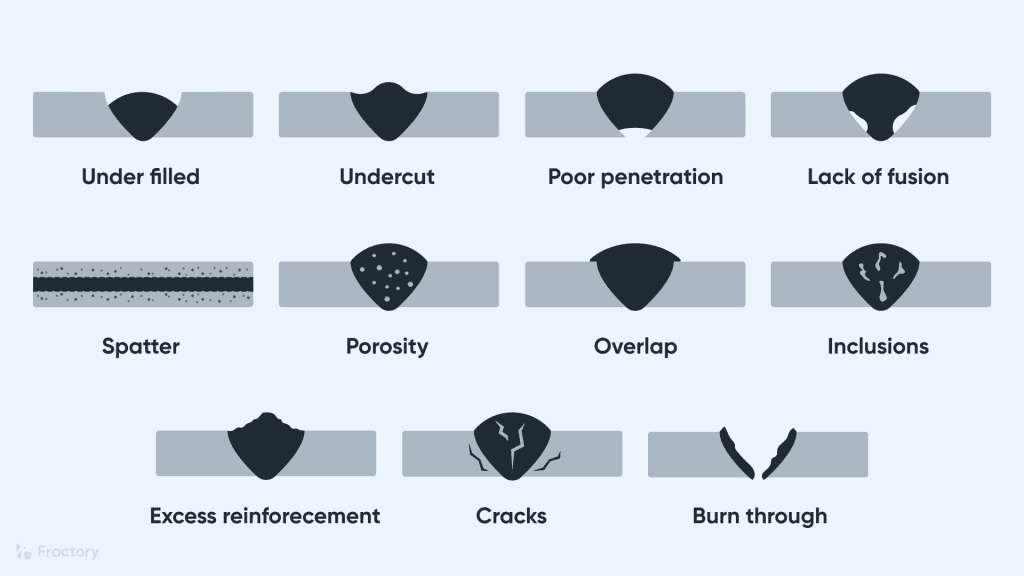
Weld inclusions can be a frustrating and costly issue in the welding process. These unwanted defects occur when foreign materials get trapped in the weld metal, compromising its strength and integrity. In this article, we will explore effective techniques and best practices that can help prevent the occurrence of weld inclusions. By understanding the root causes and implementing preventive measures, we can ensure high-quality welds and minimize the need for rework or repairs.
This image is property of www.en.hongky.com.
Review contents
Common causes of weld inclusions
Weld inclusions are a common welding defect that can compromise the strength and integrity of a weld. There are several factors that contribute to the formation of weld inclusions, and it is important to understand and address these causes in order to prevent them from occurring.
Inadequate cleaning of the base metal
One of the primary causes of weld inclusions is inadequate cleaning of the base metal. Before beginning the welding process, it is crucial to ensure that the base metal is properly cleaned to remove any impurities, contaminants, or surface oxides. Failure to do so can result in these materials being trapped within the weld, leading to inclusions.
Excessive weld pool volume
Another factor that can contribute to the formation of weld inclusions is excessive weld pool volume. When the weld pool is oversized, the risk of entrapping gases, flux, or contaminants increases, which can result in inclusions. Proper control and optimization of the weld pool volume is essential to prevent this issue.
Incorrect electrode manipulation
Improper electrode manipulation during the welding process can also lead to the formation of weld inclusions. Factors such as incorrect arc length, angle, and excessive weaving or oscillation can all contribute to the inclusion defect. It is important to use proper electrode manipulation techniques to ensure a clean and defect-free weld.
Poor joint fit-up
Poor joint fit-up is another common cause of weld inclusions. When the joint is not properly aligned, or there are gaps and irregularities between the base metal components, it becomes difficult to achieve a sound weld without entrapping foreign materials. Proper joint fit-up is crucial in preventing this type of welding defect.
Improper shielding gas usage
Lastly, improper usage of shielding gas can also contribute to the formation of weld inclusions. Shielding gas is used to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, and using the wrong gas or having an inadequate flow rate can result in inclusions. It is important to select the appropriate shielding gas and ensure proper gas flow to achieve optimal weld quality.
Prevention measures for weld inclusions
To prevent weld inclusions and ensure high-quality welds, several preventive measures can be implemented. By addressing each of the common causes mentioned above, welders can significantly reduce the risk of inclusions.
Proper preparation and cleaning of base metal
A crucial step in preventing weld inclusions is proper preparation and cleaning of the base metal. This involves removing any metal oxides, rust, and contamination that may be present on the surface. Methods such as wire brushing, grinding, or chemical cleaning can be used to achieve a clean and oxide-free surface. Additionally, it is important to prevent oil, grease, and moisture contamination, as these can also contribute to inclusions.
Optimizing weld pool volume
Achieving an optimal weld pool volume is vital in preventing inclusions. This can be done by maintaining proper welding parameters such as voltage, current, and travel speed. Using excessive filler material or allowing excessive heat input can lead to an oversized weld pool, increasing the risk of inclusions. By ensuring proper control of these parameters, welders can minimize the chances of this defect.
Correct electrode manipulation techniques
Proper electrode manipulation is critical in preventing inclusions. Welders should pay attention to factors such as arc length and angle to ensure a stable and controlled welding process. Excessive weaving or oscillation should be avoided, as it can disturb the weld pool and lead to the entrapment of foreign materials. Maintaining a consistent travel speed throughout the weld is also important in achieving a defect-free result.
Ensuring proper joint fit-up
To prevent inclusions, it is essential to ensure proper joint fit-up. This involves proper alignment of the base metal components and eliminating gaps and irregularities. Achieving a clean and smooth surface on the joint is also important, as it minimizes the chances of trapping contaminants. By taking the time to properly fit the joint before welding, welders can greatly reduce the risk of inclusions.
Effective usage of shielding gas
Proper usage of shielding gas is crucial in preventing inclusions. The appropriate type of gas should be selected based on the welding process and the materials being welded. Additionally, ensuring the proper flow rate of the shielding gas is important to achieve the desired coverage and protection of the weld pool. By following these guidelines, welders can significantly improve the quality of their welds and minimize the chances of inclusions.
Proper preparation and cleaning of base metal
To prevent weld inclusions, it is important to properly prepare and clean the base metal before welding. This involves several steps to remove any impurities, contaminants, or oxides that may be present on the surface.
Removing metal oxides
Metal oxides can form on the surface of the base metal due to exposure to air or other environmental factors. Before welding, it is important to remove these oxides using methods such as wire brushing, grinding, or chemical cleaning. Removing the oxides ensures a clean surface that promotes proper fusion and prevents the entrapment of foreign materials.
Removing rust and contamination
Rust and other forms of contamination can also hinder the welding process and increase the risk of inclusions. To prevent this, it is necessary to remove any rust or other contaminants present on the surface. This can be done through mechanical methods such as wire brushing or grinding, or through chemical cleaning techniques. By eliminating rust and contamination, welders can improve the chances of achieving a defect-free weld.
Preventing oil, grease, and moisture contamination
Oil, grease, and moisture can all contribute to weld inclusions if they are present on the surface of the base metal. These substances can react with the welding process, leading to the formation of gases or other byproducts that can become trapped in the weld. To prevent this, it is important to thoroughly clean the base metal and ensure that it remains free from these contaminants before welding. Proper storage and handling of the base metal can also help prevent oil, grease, and moisture contamination.
Optimizing weld pool volume
The size and volume of the weld pool play a significant role in the formation of weld inclusions. By optimizing the weld pool volume, welders can reduce the risk of trapping gases, flux, or contaminants within the weld.
Maintaining proper welding parameters
To achieve the desired weld pool volume, it is important to maintain proper welding parameters. This includes the appropriate voltage, current, and travel speed for the welding process and materials being used. By carefully adjusting these parameters, welders can ensure that the weld pool remains within the desired size range and minimize the chances of inclusions.
Avoiding excessive filler material
Using excessive filler material can lead to an oversized weld pool, increasing the risk of inclusions. It is important to use the appropriate amount of filler material for the joint being welded. By closely monitoring the amount of filler material used and ensuring it is in line with the weld requirements, welders can prevent the formation of inclusions.
Controlling heat input
Heat input plays a crucial role in the size and volume of the weld pool. Excessive heat input can result in an oversized weld pool, increasing the risk of inclusions. By carefully controlling the heat input through proper voltage, current, and travel speed settings, welders can achieve the optimal weld pool volume and minimize the chances of inclusions.
This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
Correct electrode manipulation techniques
Proper electrode manipulation techniques are essential in preventing weld inclusions. By using the correct arc length, angle, and avoiding excessive weaving or oscillation, welders can achieve a clean and defect-free weld.
Proper arc length and angle
Maintaining an appropriate arc length and angle is crucial in achieving a stable and controlled welding process. The arc length refers to the distance between the electrode and the base metal, and it should be carefully controlled to avoid excessive heat input or insufficient fusion. The angle at which the electrode is held can also affect the weld quality, and it is important to follow the recommended angle for the specific welding process and joint being welded.
Avoiding excessive weaving or oscillation
Excessive weaving or oscillation during the welding process can disrupt the weld pool and increase the chances of entrapment of foreign materials. It is important to maintain a steady and consistent travel path without unnecessary movement. When weaving or oscillation is required for certain welding techniques, it should be done within a controlled range to prevent disturbances to the weld pool.
Maintaining a consistent travel speed
Consistency in travel speed is essential in achieving a defect-free weld. A consistent travel speed ensures that the weld pool is properly formed and that the weld metal flows evenly. It also helps to prevent the entrapment of contaminants or inclusions within the weld. By maintaining a steady and controlled travel speed, welders can achieve high-quality welds with minimal risk of inclusions.
Ensuring proper joint fit-up
Proper joint fit-up is critical in preventing weld inclusions. By achieving proper alignment, eliminating gaps and irregularities, and obtaining a clean and smooth surface on the joint, welders can significantly reduce the risk of inclusions.
Proper alignment and gap size
Achieving proper alignment between the base metal components is essential in preventing inclusions. Improper alignment can result in gaps or irregularities that can trap foreign materials during the welding process. Welders should ensure that the joint is aligned correctly before beginning the weld to minimize the risk of inclusions.
Obtaining a clean and smooth surface
Along with proper alignment, it is important to obtain a clean and smooth surface on the joint. Any rough or contaminated surfaces can increase the risk of inclusions. By properly cleaning the joint and ensuring that it is free from any contaminants or irregularities, welders can create the ideal conditions for a defect-free weld.
Eliminating gaps and irregularities
Gaps and irregularities in the joint can significantly contribute to the formation of weld inclusions. It is important to carefully fit the joint to eliminate any gaps or irregularities that may be present. This can be achieved through proper joint preparation techniques such as grinding or machining. By eliminating gaps and irregularities, welders can ensure that the weld is free from inclusions and achieve a strong and sound joint.
This image is property of blog.transvalorusa.com.
Effective usage of shielding gas
Proper usage of shielding gas is crucial in preventing weld inclusions. By selecting the appropriate gas, ensuring the proper flow rate, and achieving good gas coverage, welders can significantly improve the quality of their welds and minimize the chances of inclusions.
Selecting the appropriate shielding gas
Different welding processes and materials require different types of shielding gases. It is important to select the appropriate gas that will provide adequate protection for the weld pool. Factors such as the type of metal being welded, the welding process being used, and the desired weld quality should all be taken into consideration when selecting the shielding gas.
Ensuring proper gas flow rate
The flow rate of the shielding gas is also important in achieving effective protection of the weld pool. Too little gas flow can result in insufficient coverage, while too much gas flow can cause turbulence or disruptions to the weld pool. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific welding process and gas being used to achieve the optimal gas flow rate.
Achieving good gas coverage
Proper gas coverage is vital in preventing inclusions. The shielding gas should effectively cover the weld pool and protect it from atmospheric contamination. Welders should ensure that the gas is reaching all areas of the weld and that there are no gaps or areas of insufficient coverage. By achieving good gas coverage, welders can create a clean and defect-free weld.
Importance of inspections and quality control
In addition to implementing preventive measures, inspections and quality control procedures play a crucial role in ensuring the absence of weld inclusions. Regular inspections and testing techniques can help detect and correct any potential issues before they result in a defective weld.
Visual inspection
Visual inspection is a fundamental quality control process that allows for the detection of surface defects, including weld inclusions. Qualified personnel should visually inspect the welds and surrounding areas to identify any signs of inclusions. This can be done using various tools such as magnifying lenses or borescopes to provide a closer examination. By conducting thorough visual inspections, welders can identify and address any potential issues in a timely manner.
Non-destructive testing
Non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques can be used to detect internal defects and ensure the integrity of the weld. Methods such as radiographic testing, ultrasonic testing, or magnetic particle testing can be employed to examine the weld for hidden inclusions or other defects that may not be visible during visual inspection. NDT techniques provide valuable information about the quality of the weld and can help identify any areas that require further attention or repair.
Quality control procedures
Implementing quality control procedures is essential in preventing weld inclusions. This includes establishing standardized processes, documenting welding procedures, and conducting regular audits to ensure compliance with quality standards. By having strict quality control measures in place, welders can identify and address any potential issues before they result in inclusions. This helps to maintain consistent weld quality and minimize the chances of defects.
This image is property of fractory.com.
Common welding techniques to prevent inclusions
Aside from the preventive measures mentioned above, there are several common welding techniques that can be employed to further prevent the occurrence of weld inclusions.
Backstep technique
The backstep technique involves welding against the direction of travel, starting from the end of the joint and progressing towards the beginning. This technique helps to push any potential inclusions or trapped gases out of the joint, resulting in a cleaner and more defect-free weld. By carefully manipulating the arc and travel speed, welders can effectively prevent inclusions using the backstep technique.
Stringer bead technique
The stringer bead technique is a welding method where the weld is made by moving the electrode in a straight line along the joint. This technique allows for precise control and minimal disturbances to the weld pool, reducing the chances of inclusions. By maintaining a steady travel speed and maintaining the correct arc length and angle, welders can achieve high-quality welds using the stringer bead technique.
Multiple-pass welding
Multiple-pass welding involves making several passes over the joint to achieve the desired weld strength and quality. By using multiple passes, welders can control the weld pool size and improve the fusion between the base metal components. This technique allows for better control and reduces the risk of inclusions. Proper electrode manipulation and control of welding parameters are crucial in achieving successful multiple-pass welds.
Peening technique
The peening technique involves the mechanical working or tapping of the weld immediately after it has solidified. This technique helps to relieve stresses and improve the fusion between the weld metal and the base metal. By using the peening technique, welders can enhance the integrity of the weld and reduce the risk of inclusions. It is important to apply the peening technique with care and avoid excessive force or distortion during the process.
Conclusion
Preventing weld inclusions is essential in ensuring the structural integrity and performance of a weld. By addressing the common causes of weld inclusions, implementing proper preventive measures, and employing suitable welding techniques, welders can significantly reduce the risk of this welding defect. Proper preparation and cleaning of the base metal, optimizing weld pool volume, correct electrode manipulation techniques, ensuring proper joint fit-up, effective usage of shielding gas, and implementing inspections and quality control procedures are all crucial aspects in preventing weld inclusions. By following these guidelines and maintaining a focus on quality, welders can achieve defect-free welds that meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.
This image is property of www.en.hongky.com.