Weld distortion can be a pesky problem, causing headaches for many welders out there. It’s frustrating to spend hours perfecting a weld, only to have it warp or distort after the process. But fear not, because in this article, we will reveal some useful tips and tricks on how to prevent weld distortion. Whether you’re a professional welder or just a DIY enthusiast, these techniques will surely come in handy to ensure your welded joints stay intact and distortion-free. So grab your welding helmet and let’s dive into the world of weld distortion prevention!
This image is property of cdn.canadianmetalworking.com.
Review contents
Understanding Weld Distortion
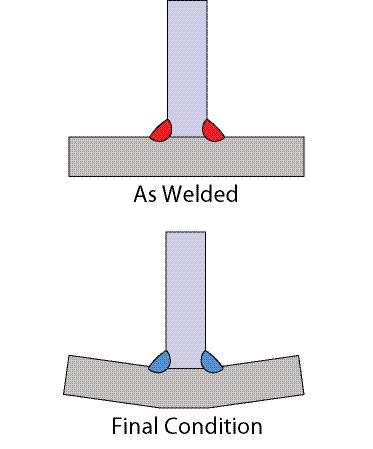
Weld distortion refers to the changes in the dimensions of a welded structure due to the heat input during the welding process. It can cause misalignment, warping, and residual stresses, which can negatively impact the structural integrity and functionality of the welded component. In order to prevent weld distortion, it is crucial to understand the causes and types of weld distortion.
Causes of Weld Distortion
Several factors contribute to weld distortion, including:
-
Heat input: The intense heat generated during welding leads to localized expansion and contraction, causing the material to deform.
-
Residual stresses: The non-uniform distribution of stresses in the welded joint can result in distortion.
-
Joint design: Poor joint design, such as inadequate bevel angles or improper fit-up, can lead to uneven cooling and subsequent distortion.
-
Welding technique: Inappropriate welding techniques, such as excessive weaving or improper travel speed, can result in distortion.
-
Material properties: The properties of the base material, such as its thickness and thermal conductivity, can influence the degree of distortion.
Types of Weld Distortion
Weld distortion can manifest in different forms, including:
-
Angular distortion: This occurs when the welded structure becomes misaligned or warped along its longitudinal axis.
-
Transverse distortion: In transverse distortion, the welded component bends or twists perpendicular to the weld line.
-
Buckling distortion: Buckling distortion happens when the welded joint collapses or deforms due to uneven stresses.
-
Bowing distortion: Bowing distortion refers to the deformation in the form of a convex or concave shape along the length of the weld.
Preventing Weld Distortion
While weld distortion cannot be entirely eliminated, there are several preventive measures that can be employed to minimize its occurrence. These measures encompass various aspects, from proper joint preparation to selecting the right welding method.
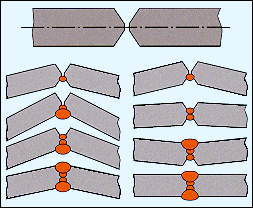
Proper Joint Preparation
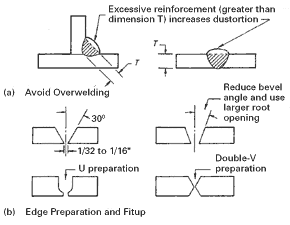
Good joint preparation plays a significant role in preventing weld distortion. It involves thorough cleaning and surface preparation of the base materials to eradicate any contaminants that can negatively affect the integrity of the weld. Additionally, proper joint fit-up and design, including appropriate bevel angles and root gaps, ensure better control over heat input and reduce the likelihood of distortion.
Controlling Heat Input
Controlling heat input is crucial in minimizing weld distortion. Parameters such as welding voltage, amperage, and travel speed should be carefully selected to achieve the optimal heat input for the specific application. Welding processes with lower heat input, such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) or laser welding, are generally preferred for materials prone to distortion.
Welding Sequence and Technique
The welding sequence and technique employed during the welding process can greatly influence the occurrence of weld distortion. Utilizing a symmetrical welding sequence, where the welds are applied evenly on both sides of a joint, helps distribute the heat input more evenly, reducing distortion. Employing a balanced welding technique, with controlled travel speed and proper weaving, also aids in minimizing distortion.
Clamping and Fixturing
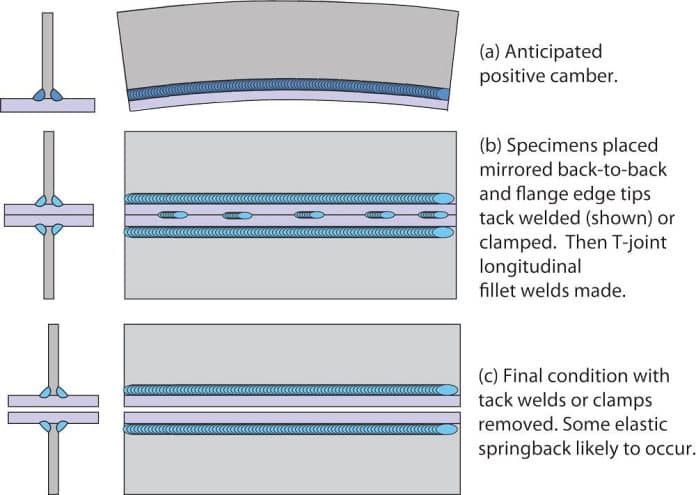
Proper clamping and fixturing of the weldment are essential to prevent distortion. Clamps and fixtures hold the materials in place during welding, ensuring alignment and minimizing movement caused by heat input. Additionally, implementing tack welds at strategic locations prior to welding helps secure the joint and reduce the chances of distortion.
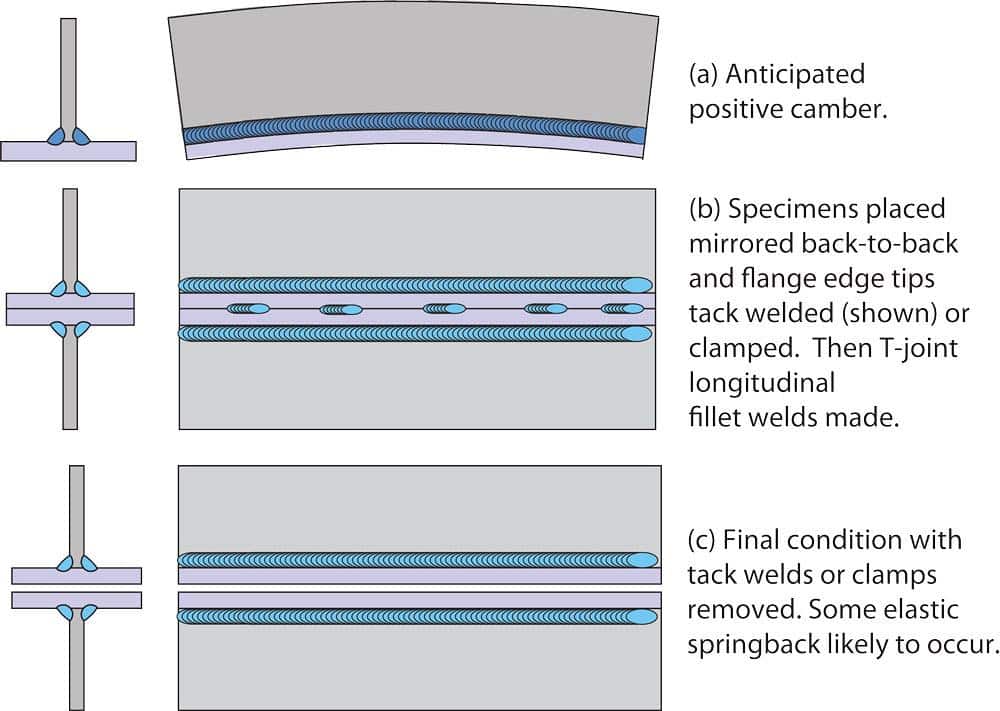
Preventing Warping
Warping, a common form of distortion, can be prevented by utilizing heat sinks. Heat sinks help distribute heat away from the weld zone, reducing the localized expansion and contraction that leads to warping. Additionally, careful consideration of the welding direction, starting from the center and progressing outwards, can help minimize warping.
Minimizing Residual Stresses
Minimizing residual stresses is vital for preventing distortion. Welding with lower heat input reduces the magnitude of these stresses, as excessive heat can induce higher thermal expansion and contraction. Post-weld heat treatment processes, such as stress relieving, can also be employed to relieve residual stresses and minimize distortion.
Avoiding Overwelding
Overwelding, the excessive deposition of weld metal, can increase the heat input and subsequently cause distortion. It is crucial to follow welding specifications and ensure controlled weld deposit, avoiding unnecessary excessive weld metal that can lead to distortion.
Using Preheat and Post-heat Techniques
Preheating the base material before welding can help minimize distortion by reducing the temperature gradient between the weld zone and the surrounding material. Similarly, post-heating techniques can relieve residual stresses and mitigate distortion. Proper selection and application of preheat and post-heat techniques are essential for successful distortion prevention.
Selecting the Right Welding Method
Choosing the appropriate welding method is vital in preventing distortion. Different welding processes have varying heat inputs and characteristics, which can considerably impact distortion. Understanding the material properties and requirements of the application helps in selecting the most suitable welding method that minimizes distortion.
Using Back Purging for Welding
Back purging is a technique used to protect the backside of a weld joint from oxidation and contamination. It involves supplying an inert gas, such as argon, to displace the surrounding air and create a gas shield. Back purging is particularly effective in preventing distortion in materials sensitive to oxidation, such as stainless steel or titanium.
Proper Joint Preparation
Proper joint preparation is a fundamental step in preventing weld distortion. It encompasses two key aspects: cleaning and surface preparation, and joint design and fit-up.
Cleaning and Surface Preparation
Thorough cleaning and surface preparation of the base materials are crucial to ensure a clean welding environment and a sound weld. Any contaminants, such as rust, oil, grease, or paint, should be removed using appropriate cleaning methods, such as wire brushing, degreasing solvents, or sandblasting. Surface preparation techniques, such as grinding or chamfering, can also be employed to create clean and suitable surfaces for welding.
Joint Design and Fit-up
The design and fit-up of the joint significantly impact the welding process and subsequent distortion. Proper joint design includes considerations such as the type of joint, bevel angles, root gaps, and weld sizes. A well-designed joint allows for better heat distribution, uniform cooling, and reduced residual stresses, resulting in less distortion. Additionally, ensuring proper fit-up, including alignment and tight fit between the parts to be welded, plays a crucial role in preventing distortion.
Controlling Heat Input
Controlling heat input during welding is essential to minimize distortion. This involves careful selection of appropriate welding parameters and the welding process itself.
Appropriate Welding Parameters
The welding parameters, such as voltage, amperage, and travel speed, directly influence the heat input. It is essential to choose appropriate parameters for the specific welding application and material being welded. By optimizing the welding parameters, the heat input can be controlled, reducing the likelihood of distortion.
Proper Selection of Welding Process
Different welding processes have varying heat inputs and characteristics, making the selection of the right process critical in preventing distortion. Processes with lower heat inputs, such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) or laser welding, are preferable for materials prone to distortion. Understanding the material properties, joint requirements, and application-specific factors aids in choosing the most suitable welding process.
This image is property of www.lincolnelectric.com.
Welding Sequence and Technique
The welding sequence and technique employed during the welding process play a crucial role in preventing distortion.
Symmetrical Welding Sequence
Utilizing a symmetrical welding sequence minimizes distortion by distributing the heat input evenly on both sides of the joint. This helps maintain balance and prevents excessive localized expansion and contraction. By starting the welds from the center and progressing outwards in a controlled manner, the symmetrical welding sequence helps reduce distortion.
Balanced Welding Technique
Implementing a balanced welding technique involves carefully controlling the travel speed, weaving, and other welding parameters. Consistency in the application of the welds ensures a uniform heat input, reducing distortion. By avoiding excessive weaving or unstable travel speeds, a balanced welding technique aids in preventing distortion and maintaining the integrity of the welded joint.
Clamping and Fixturing
Proper clamping and fixturing of the weldment are crucial in minimizing distortion. This involves the use of clamps, fixtures, and tack welds.
Using Clamps and Fixtures
Clamps and fixtures hold the parts securely in place during welding, minimizing movement and misalignment caused by heat input. These tools ensure proper alignment and reduce the likelihood of distortion. Utilizing clamps and fixtures suitable for the specific welding application aids in achieving a stable and distortion-free weld.
Implementing Tack Welds
Tack welds are preliminary welds used to temporarily hold the joint in place before the final welding. By strategically placing tack welds at key locations, the joint can be secured, reducing the chances of movement and misalignment during welding. Tack welds also aid in maintaining the desired fit-up and controlling distortion.
This image is property of cdn.canadianmetalworking.com.
Preventing Warping
Warping is a common form of distortion that can be prevented by employing certain techniques, such as using heat sinks and strategic welding direction.
Use of Heat Sink
A heat sink is a device used to absorb or dissipate heat, preventing its concentration in the weld zone. By applying a heat sink, such as copper or aluminum blocks, near the weld area, the localized expansion and contraction can be controlled. This helps minimize warping by distributing the heat more evenly throughout the surrounding material.
Strategic Welding Direction
The welding direction can significantly impact the occurrence of warping. By starting the weld in the center and progressing outwards, the contraction forces are balanced, reducing the likelihood of warping. Strategic welding direction helps achieve even cooling and minimizes the distortion caused by uneven stresses.
Minimizing Residual Stresses
Minimizing residual stresses is crucial in preventing distortion and maintaining the integrity of the welded joint. Several techniques can be employed to achieve this, including welding with lower heat input, post-weld heat treatment, and stress-relieving techniques.
Welding with Lower Heat Input
Excessive heat input during welding can lead to higher thermal expansion and contraction, resulting in higher residual stresses and distortion. By choosing welding processes with lower heat inputs, the magnitude of these stresses can be minimized. Processes such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) or laser welding are suitable options for materials prone to distortion.
Post-weld Heat Treatment
Post-weld heat treatment techniques, such as stress relieving, can help reduce residual stresses and distortion. Stress relieving involves applying controlled heat to the welded component, followed by gradual cooling. This process helps alleviate residual stresses, contributing to reduced distortion and improved dimensional stability.
Stress-relieving Techniques
Apart from post-weld heat treatment, various stress-relieving techniques can be employed to minimize residual stresses. These techniques include vibratory stress relief, which utilizes controlled vibrations to reduce stresses, and shot peening, which induces compressive stresses on the surface of the weldment. Implementing stress-relieving techniques helps alleviate stresses and minimize distortion.
This image is property of www.twi-global.com.
Avoiding Overwelding
Overwelding, the excessive deposition of weld metal, can increase the heat input and contribute to distortion. To avoid overwelding, it is essential to adhere to welding specifications and employ controlled weld deposit techniques.
Follow Welding Specifications
Adhering to welding specifications ensures that the appropriate weld size and strength are achieved without unnecessary overwelding. Welding procedures and guidelines provided by welding codes and standards should be followed to ensure the proper deposition of weld metal. Strict adherence to welding specifications helps control the heat input, reducing the likelihood of distortion.
Controlled Weld Deposit
Controlling the amount of weld metal deposited is crucial in preventing overwelding and subsequent distortion. By carefully monitoring the weld deposition rate and filler metal usage, excess heat input can be avoided. Employing appropriate techniques, such as controlling the wire feed speed or electrode size, aids in achieving controlled weld deposits that minimize distortion.
Using Back Purging for Welding
Back purging is a technique used to protect the backside of a weld joint from oxidation and contamination, particularly in materials sensitive to oxidation, such as stainless steel or titanium.
Definition and Purpose
Back purging involves the use of an inert gas, typically argon, to displace the surrounding air and create a protective gas shield on the backside of the weld. This shielding prevents oxidation and contamination during the welding process. Back purging is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the weld and preventing distortion, particularly in materials susceptible to oxidation.
Back Purging Techniques
Various back purging techniques can be employed, depending on the specific welding application and joint configuration. These techniques include using dams or backing strips to confine the inert gas to the weld area, as well as employing specialized purge chambers or inflatable bladders to create a confined purging environment. Each technique ensures the backside of the weld is shielded, preventing oxidation and minimizing distortion.
In conclusion, weld distortion is a common challenge faced during the welding process. However, by understanding the causes and types of distortion and implementing preventive measures, such as proper joint preparation, controlling heat input, employing suitable welding techniques, and using back purging when necessary, the occurrence of distortion can be minimized. Taking a comprehensive approach to preventing weld distortion ensures high-quality, strong, and distortion-free welds, contributing to the overall success of welding projects.
This image is property of www.lincolnelectric.com.