In the world of welding, selecting the correct welding rod for a project can make all the difference between a successful weld and a complete disaster. With numerous options available in the market, it can be overwhelming to determine which rod is best suited for your specific project. From understanding the different types of welding rods to considering factors such as material, electrode size, and welding technique, our comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to choose the right welding rod every time. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of welding rods and discover the key factors to consider for flawless welds!
Review contents
Factors to Consider
When selecting the appropriate welding rod for a project, several factors should be considered. These factors will influence the overall success and quality of the weld, as well as the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the welding process. By carefully weighing these factors, we can ensure that we choose the right welding rod for each specific welding task.
Material Type
The type of material being welded is a critical consideration when choosing a welding rod. Different welding rods are designed to work with specific materials, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, cast iron, copper, brass, and nickel alloys. Each material has its own unique properties and characteristics, requiring a welding rod that is compatible with its composition.
Joint Type
The joint type is another important factor to consider. The welding rod must be able to provide adequate penetration and fusion for the specific joint configuration. Common joint types include butt joints, T-joints, corner joints, and overlap joints. Each joint type requires a different approach and may necessitate the use of a specific welding rod.
Welding Position
The welding position refers to the orientation of the weld joint relative to gravity. There are four main welding positions: flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead. The chosen welding rod must be suitable for the specific welding position to ensure optimal weld quality and penetration. Welding rods are often classified and recommended based on their ability to perform in different positions.
Power Source
The power source used for welding is crucial in determining the appropriate welding rod. The most common power sources include stick welding (SMAW), MIG welding (GMAW), TIG welding (GTAW), and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW). Each power source has its own unique characteristics and requirements, and the chosen welding rod should align with the capabilities of the selected power source.
Base Metal Thickness
The thickness of the base metal being welded is a vital consideration. Using the correct welding rod is essential to achieve proper fusion and avoid issues such as burn-through or inadequate penetration. Different welding rods are designed to handle various base metal thicknesses, such as thin metal, medium metal, and thick metal. Choosing the right welding rod ensures a strong and reliable weld.
Welding Technique
The welding technique employed plays a significant role in determining the appropriate welding rod. Different welding techniques, such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW), have distinct requirements and characteristics. The welding rod selected should be compatible with the chosen welding technique for optimal results.
Environment and Conditions
The environment and conditions in which the welding will take place also impact the choice of welding rod. Welding can be performed both indoors and outdoors, each requiring different considerations. Factors like weather conditions and the presence of contaminants can affect the welding process and the choice of welding rod. It is essential to select a welding rod that can withstand these environmental factors and produce a high-quality weld.
Cost
Cost is an important factor that cannot be overlooked. Different welding rods vary in price, and the overall cost of a project can be influenced by the choice of welding rod. While it is crucial to select a welding rod that meets the project’s requirements, considering cost-effectiveness and budget constraints is also necessary. Finding a balance between quality and cost is key when choosing the right welding rod.
Availability
The availability of specific welding rods is another factor to consider. Some welding rods may be readily available, while others may require ordering or special procurement. It is essential to consider the local availability of welding rods to ensure convenient and timely access to the necessary materials. Planning ahead and considering availability can help avoid project delays.
Skill Level
The skill level of the welder must also be taken into account. Certain welding rods are better suited for beginners, while others require more advanced skills to produce satisfactory results. Matching the welding rod to the welder’s skill level ensures that the welder can work efficiently and effectively, leading to better weld quality and overall project success.
Understanding Welding Rods
To choose the right welding rod, it is essential to have a good understanding of their different types, coating compositions, classification system, and sizing. By familiarizing ourselves with these aspects, we can make an informed decision when selecting a welding rod for our specific welding project.
Types of Welding Rods
There are various types of welding rods available, each designed for specific applications and materials. Common types of welding rods include carbon steel rods, stainless steel rods, aluminum rods, cast iron rods, copper and brass rods, and nickel alloy rods. Understanding the characteristics and purposes of each type of welding rod enables us to choose the most suitable one for our project.
Coating Compositions
Welding rods have different coatings that serve specific purposes during the welding process. The coating can provide protection against atmospheric contamination, improve arc stability, control the weld’s mechanical properties, and contribute to slag formation. The coating compositions vary depending on the type of welding rod and its intended application. Understanding the coating compositions allows us to choose a welding rod that best meets our project’s requirements.
Classification System
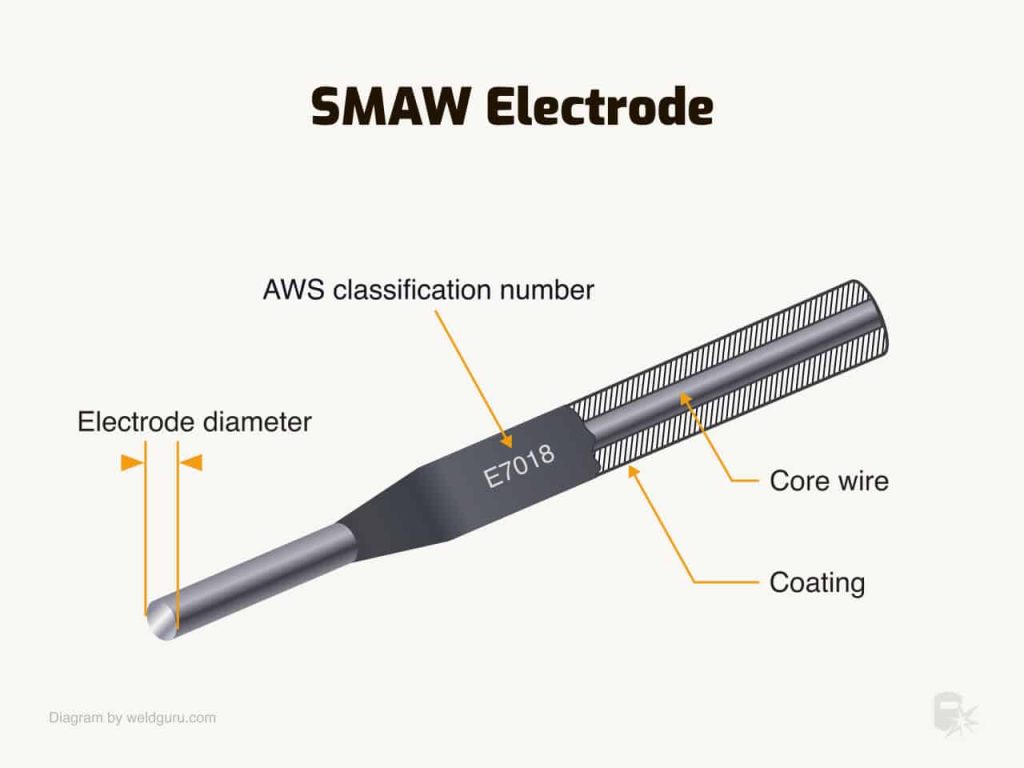
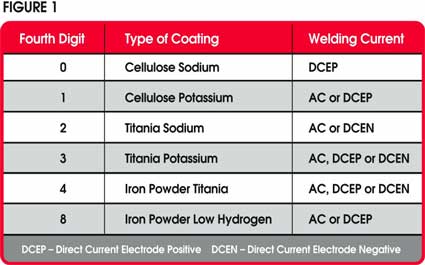
Welding rods are classified based on their properties and intended applications. The most common classification system is the American Welding Society (AWS) system, which uses a combination of letters and numbers to indicate the welding rod’s characteristics. The classification provides information about the welding rod’s tensile strength, positions it can be used in, and the welding techniques it is compatible with. Familiarizing ourselves with the classification system helps us select a welding rod that aligns with our project’s specifications.
Rod Size
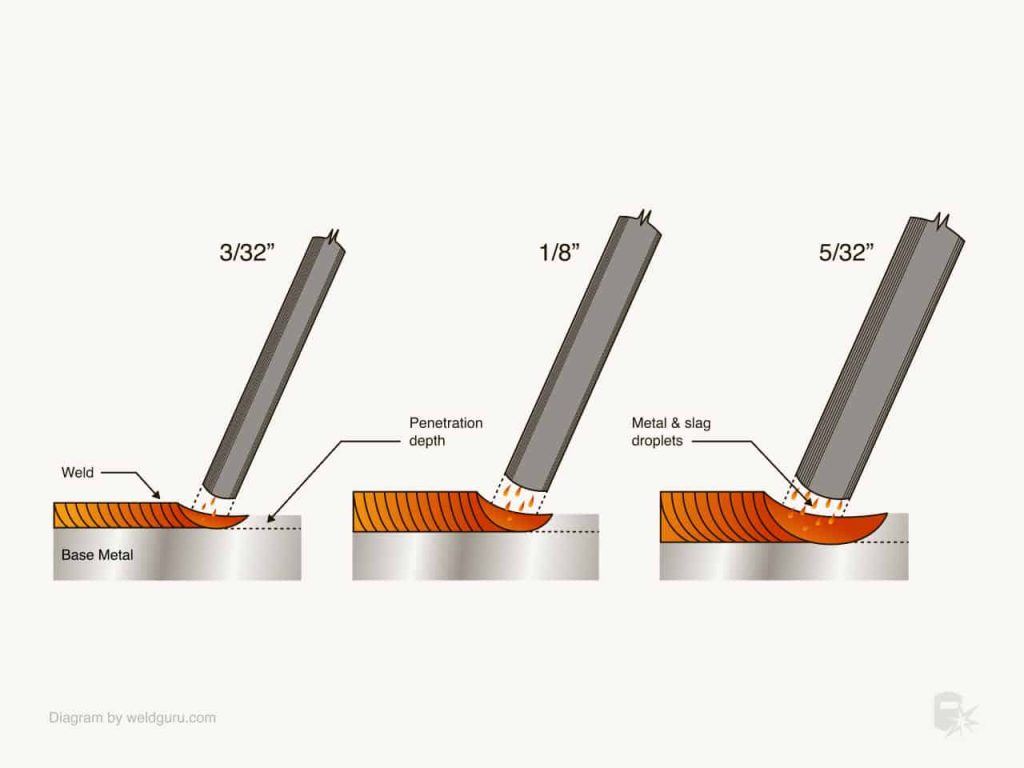
Welding rods come in various sizes to accommodate different welding applications and base metal thicknesses. The size of a welding rod is determined by its diameter, typically measured in inches or millimeters. The choice of rod size depends on the welding project’s requirements, including the base metal thickness and the desired weld strength. Selecting the right rod size ensures proper heat distribution and fusion, resulting in a high-quality weld.
This image is property of dnhsecheron-home.s3.amazonaws.com.
Matching Rods to Materials
To achieve optimal weld quality and performance, it is crucial to match the welding rod to the specific materials being welded. Different materials have different compositions and properties, requiring welding rods that can effectively join them together.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a commonly welded material that requires welding rods specifically designed for carbon steel applications. These welding rods typically have a carbon content equivalent (C.E.) to match the carbon content of the base metal. Choosing the appropriate carbon steel welding rod ensures a strong, durable, and crack-resistant weld.
Stainless Steel
Welding stainless steel requires welding rods specifically formulated for stainless steel applications. Stainless steel welding rods are designed to provide corrosion resistance, high strength, and excellent weld characteristics. They are available in various compositions, such as austenitic, ferritic, and martensitic stainless steels, to suit different stainless steel alloys.
Aluminum
Aluminum welding rods are specifically designed for welding aluminum and its alloys. These welding rods typically contain a high percentage of aluminum and other alloying elements to ensure proper weld fusion and strength. Aluminum welding rods often have a special coating that prevents oxide formation, which can negatively impact the weld quality.
Cast Iron
Welding cast iron is a unique process that requires welding rods specifically formulated for cast iron applications. Cast iron welding rods have a high nickel content, which helps achieve good fusion between the welding rod and the cast iron base metal. The low-heat input associated with cast iron welding rods is essential in preventing cracking and maintaining the integrity of the cast iron.
Copper and Brass
Copper and brass welding requires welding rods specifically designed for these materials. Copper and brass welding rods contain alloying elements that ensure proper fusion, strength, and corrosion resistance. These welding rods are available in various compositions to match the specific copper or brass alloy being welded.
Nickel Alloys
Nickel alloy welding rods are formulated to join nickel alloys together while maintaining the alloys’ unique properties. These welding rods contain nickel as the main component and may contain other elements such as chromium, molybdenum, or tungsten. Matching the appropriate nickel alloy welding rod to the specific nickel alloy being welded ensures the integrity and performance of the welded joint.
By understanding the specific requirements of each material, we can choose the right welding rod that will provide a strong, reliable, and durable weld.
Determining Joint Type
The joint type plays a crucial role in determining the welding rod that should be used. Different joint configurations require specific welding techniques and welding rod characteristics to achieve a successful weld.
Butt Joint
A butt joint is a common joint configuration where two pieces of metal are joined along their edges. Butt joints require good penetration and fusion along the entire joint length. To achieve this, welding rods with excellent penetration capabilities and a high deposition rate are typically recommended for butt joint welding.
T-Joint
In a T-joint, one piece of metal is perpendicular to the other, forming a T-shaped configuration. T-joints require welding rods that can properly fill the gap between the two metal pieces and create a strong weld. Welding rods with good gap-filling properties and a smooth arc are often used for T-joint welding.
Corner Joint
A corner joint is formed when two metal pieces meet at a right angle, creating a corner. Corner joints often require welding rods with good control and maneuverability to effectively join the metal pieces. Welding rods with excellent arc stability and control are typically chosen for corner joint welding.
Overlap Joint
An overlap joint occurs when one piece of metal overlaps another, creating a lap at the joint. Overlap joints require welding rods that can effectively fuse the overlapping metal pieces without excessive heat input. Welding rods with good fusion characteristics and a stable arc are commonly used for overlap joint welding.
By understanding the different joint types and their specific welding requirements, we can select the appropriate welding rod that will ensure a strong and reliable weld.
This image is property of weldguru.com.
Considering Welding Positions
The welding position refers to the orientation of the weld joint relative to gravity. Different welding positions require different welding rods to achieve optimal weld quality and penetration.
Flat Position
In the flat position, the weld joint lies horizontally, parallel to the ground. This is the easiest position for welding and requires welding rods that provide good control, puddle stability, and slag control. Welding rods with stable and predictable arc characteristics are often recommended for flat position welding.
Horizontal Position
In the horizontal position, the weld joint lies either vertically or overhead. Horizontal position welding requires welding rods that can provide good penetration and fusion despite the potential challenges posed by gravity. Welding rods with good out-of-position welding capabilities and self-shielded flux are commonly chosen for horizontal position welding.
Vertical Position
In the vertical position, the weld joint is oriented vertically, either upwards or downwards. Vertical position welding is more challenging than flat or horizontal position welding due to the increased effects of gravity. Welding rods with excellent vertical welding characteristics, such as good slag control and solid deposition rates, are typically used for vertical position welding.
Overhead Position
In the overhead position, the weld joint is located above the welder’s head. Overhead position welding presents significant challenges, including the risk of weld defects and the need for precise control. Welding rods with low spatter and good control are generally preferred for overhead position welding.
By selecting welding rods that are suitable for the specific welding position, we can ensure that the weld quality and penetration meet the desired standards.
Matching Power Source
The power source used for welding is a crucial factor to consider when choosing a welding rod. Different power sources have distinct characteristics and requirements, determining the appropriate welding rod for efficient and effective welding.
Stick Welding
Stick welding, or shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), is a popular welding process that uses a consumable electrode covered in a flux to create the weld. Stick welding requires welding rods that can withstand high amperage settings and provide good arc stability. Welding rods with strong arc ignition and deep penetration are often used for stick welding applications.
MIG Welding
MIG welding, or gas metal arc welding (GMAW), utilizes a continuously fed wire electrode and a shielding gas to protect the molten weld pool. MIG welding requires welding rods that can feed smoothly and provide good arc stability. The selected MIG welding rod should match the specific welding wire being used to ensure proper fusion and deposition.
TIG Welding
TIG welding, or gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a shielding gas to create the weld. TIG welding requires welding rods that are compatible with the specific base metal being welded and can provide good arc stability and fusion control. The chosen TIG welding rod should match the base metal composition and thickness for optimal results.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding
Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) utilizes a continuously fed wire electrode with a flux-filled center to produce the weld. FCAW can be performed with or without shielding gas, depending on the specific welding requirements. Welding rods for FCAW should be selected based on whether the process is gas-shielded or self-shielded, as the welding rod composition will differ accordingly.
By considering the power source being used, we can select welding rods that are compatible with the welding equipment and will deliver the desired results.
This image is property of www.weldingandndt.com.
Understanding Base Metal Thickness
The thickness of the base metal being welded is an essential factor when choosing the right welding rod. Different welding rods are designed to handle specific base metal thicknesses, ensuring proper fusion and penetration.
Thin Metal
When welding thin metal, welding rods with lower current settings and excellent control are typically used. These welding rods help prevent burn-through and ensure adequate fusion and penetration without damaging the base metal. Choosing the correct welding rod for thin metal ensures a strong and aesthetically pleasing weld.
Medium Metal
Welding medium-thickness metal requires welding rods that can provide the necessary heat input and penetration. These welding rods should offer good deposition rates and control to achieve a quality weld in a reasonable time frame. Selecting the appropriate welding rod for medium metal ensures a durable, structurally sound weld.
Thick Metal
Thick metal welding necessitates welding rods with higher current settings and a higher deposition rate. These welding rods can generate the necessary heat to penetrate the thick base metal and create a strong weld. Properly selecting welding rods for thick metal ensures the weld’s integrity, strength, and long-term durability.
By accurately assessing the base metal thickness, we can choose welding rods that are specifically designed for the specific thickness range, resulting in successful and reliable welds.
Choosing the Right Welding Technique
Different welding techniques require specific welding rods to achieve the desired results. By understanding the characteristics and requirements of each welding technique, we can select the appropriate welding rod for optimal performance.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Shielded Metal Arc Welding, commonly known as stick welding, relies on a consumable electrode covered in a flux coating. Stick welding rods are designed for this technique, providing the necessary flux to protect the weld pool and ensuring good penetration. The choice of stick welding rod can vary based on the specific application, such as general purpose rods for mild steel or specialized rods for stainless steel or cast iron.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Gas Metal Arc Welding, or MIG welding, uses a continuously fed wire electrode and a shielding gas to protect the weld from atmospheric contamination. MIG welding requires welding rods that are compatible with the welding wire being used. These welding rods deliver the necessary alloying elements and flux to ensure proper fusion and deposition. The selection of MIG welding rods should align with the base metal composition and the desired welding characteristics.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, also known as TIG welding, employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a shielding gas to create the weld. TIG welding rods are usually made from the same material as the base metal and do not contribute to the weld pool. The purpose of TIG welding rods is to facilitate the welding process, provide additional alloying elements, and control the weld pool. Properly choosing TIG welding rods ensures excellent arc stability and precise control over the weld.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Flux-Cored Arc Welding can be performed either with or without shielding gas, depending on the specific requirements. FCAW welding rods have a flux-filled center, which contributes to the weld’s protection and facilitates the welding process. FCAW welding rods can be classified as gas-shielded or self-shielded, with different compositions to suit the welding application. The selection of the appropriate FCAW welding rod depends on the desired weld characteristics and the availability of shielding gas.
By matching the welding technique to the welding rod, we can ensure the compatibility of the two and achieve the desired results.
This image is property of weldguru.com.
Considering Environment and Conditions
The environment and conditions in which welding takes place can influence the choice of welding rod. Factors such as indoor vs. outdoor welding, weather conditions, and the presence of contaminants should be taken into account when selecting the appropriate welding rod.
Indoor vs. Outdoor
Indoor and outdoor welding may have different requirements due to variations in ventilation, airflow, and exposure to external elements. When welding indoors, factors such as adequate ventilation and fume extraction should be considered. Outdoor welding, on the other hand, may require welding rods that are more resistant to wind, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Selecting welding rods that can withstand the specific environmental conditions ensures optimal performance and weld quality.
Weather Conditions
Weather conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed, can affect the welding process and the choice of welding rod. In cold weather, welding rods that can maintain good arc stability and fusion properties at low temperatures are recommended. High humidity can introduce moisture into the welding process, necessitating the use of welding rods with low moisture absorption. Windy conditions may require welding rods with higher deposition rates and better wind-resistance properties. Considering the weather conditions when choosing a welding rod ensures successful welding under various environmental circumstances.
Presence of Contaminants
The presence of contaminants, such as oils, paints, rust, or dirt, in the welding environment can impact the welding process and the choice of welding rod. Contaminants can affect the weld’s quality, integrity, and appearance. Selecting welding rods with appropriate fluxes or coatings can help mitigate the adverse effects of contaminants and ensure clean, sound welds. Proper cleaning and preparation of the base metal, in combination with the right welding rod, can result in high-quality welds even in the presence of contaminants.
By considering the specific environmental conditions and factors that may influence the welding process, we can choose welding rods that are best suited for the given situation.
Assessing Skill Level
The skill level of the welder should be taken into account when selecting a welding rod. Different welding rods have varying levels of difficulty and skill requirements. It is essential to match the welding rod’s complexity to the welder’s skill level to ensure successful welds and a positive welding experience.
Beginner-friendly Rods
For beginners with limited welding experience, it is advisable to start with welding rods that are easy to use and forgiving. Welding rods with good arc stability, wide operating ranges, and excellent weld pool control are ideal for beginner welders. These rods provide a comfortable learning curve and allow beginners to develop their skills while still achieving decent weld quality.
Intermediate-level Rods
As welders gain experience and proficiency, they can progress to welding rods that offer more control and possibilities for customization. Intermediate-level rods may require more precise control and technique to achieve optimal weld results. However, with the right skill set, intermediate-level rods can provide welders with more flexibility and the ability to tackle a broader range of welding projects.
Advanced Rods
Advanced welding rods are typically reserved for experienced welders who have mastered their welding techniques and possess extensive knowledge in diverse welding applications. These rods often require highly refined skills and specific welding techniques. Advanced rods may offer superior weld quality, enhanced mechanical properties, or niche capabilities. Experienced welders can benefit from these rods to deliver exceptional results in specialized welding projects.
By aligning the welding rod’s complexity with the welder’s skill level, we can ensure that the welding process remains enjoyable, efficient, and successful.
In conclusion, selecting the right welding rod for a project involves considering various factors, such as material type, joint type, welding position, power source, base metal thickness, welding technique, environment and conditions, cost, availability, and skill level. By carefully evaluating these factors and understanding the properties and requirements of different welding rods, we can make informed decisions that result in high-quality welds and successful welding projects.
This image is property of www.millerwelds.com.